
In the dynamic sphere of education and professional development, a singular constant remains: instructional design. This precise blend of art and science crafts immersive learning experiences that go beyond simple information transfer. Instructional design is the guiding force behind contemporary education and training, creating experiences that not only relay knowledge but also kindle comprehension and promote mastery.
In our fast-paced society, where information is readily available, yet true understanding is the ultimate pursuit, effective instructional design becomes the crucial element in amplifying learning outcomes. It’s the hidden mechanism that opens the pathway to profound, impactful learning, ensuring that acquired knowledge is not merely retained but actively utilized. From traditional classrooms to digital platforms, the influence of instructional design echoes throughout all learning environments.
This piece embarks on an exploration of instructional design, shedding light on its diverse role in today’s education and training. We will excavate its roots, delving into the science of learning that forms its foundation. We will unravel the complex process of instructional design, discussing the methodologies and strategies that morph information into transformation. Additionally, we will traverse the technology-driven landscape, highlighting how instructional design consistently evolves to address the changing needs of learners.
Join us as we reveal the artistry and methodology behind instructional design, showing how it holds the key to unlocking your learning potential and transforming the way we obtain knowledge and skills in the 21st century.
Mastering Instructional Design ─ The Blueprint of Effective Learning

Instructional design, at its essence, is the intricate process of fashioning effective, immersive learning experiences. It’s an art form and scientific discipline centered on the creation of educational materials and activities that optimize comprehension, memory retention, and the practical application of knowledge. Drawing an analogy, instructional designers are architects of learning, crafting blueprints tailored to a diverse range of audiences, topics, and objectives.
The foundations of instructional design are rooted in an in-depth comprehension of human learning processes. These principles tap into a myriad of learning theories including behaviorism, cognitivism, constructivism, and connectivism. Instructional design aims to align experiences with these theories, thereby facilitating learners in understanding concepts, drawing connections, and honing vital skills effectively.
Tracing the Evolution of Instructional Design ─ A Historical Overview
Instructional design’s lineage can be traced back to the dawn of the 20th century, with thought leaders like Edward Thorndike and B.F. Skinner laying the foundation for behaviorist learning theories. Their groundbreaking proposition that learning is an outcome of stimulus and response significantly shaped the early contours of instructional design.
The evolution of instructional design kept pace with the advancements in educational psychology and technology. The 1950s saw the emergence of programmed instruction, a forerunner to computer-based learning. In the following decade, Robert Gagné unveiled his ‘nine events of instruction’, underlining the significance of engaging learners through diverse media and activities.
The 1970s witnessed the rise of systematic instructional design models like ADDIE (Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation, Evaluation), offering a structured framework to craft effective learning experiences. This model became the keystone of instructional design and continues to hold sway today.
In the present digital era, instructional design has embraced technology, multimedia, and e-learning platforms. As edtech continues to evolve, instructional designers leverage its potential to forge interactive and immersive learning experiences.
The Pivotal Role of Instructional Designers in Shaping Educational Experiences
Instructional designers are the custodians of modern education and training. They serve as the architects of learning, translating educational objectives into tangible, engaging experiences. Their role extends beyond mere transmission of information; it encapsulates understanding learners’ needs, designing effective assessments, and perpetually enhancing the learning process.
Instructional designers work in tandem with subject-matter experts, educators, and technologists to create exhaustive educational materials. Their skill set is diverse, melding creativity with a profound comprehension of pedagogy and technology. They are the change-makers, continuously adapting and innovating to cater to the emerging needs of learners in a dynamic educational landscape.
In the ensuing sections, we will delve deeper into the science of learning, the instructional design process, and the exhilarating potential of technology in reshaping educational experiences.
Instructional Design Process ─ An In-Depth Look
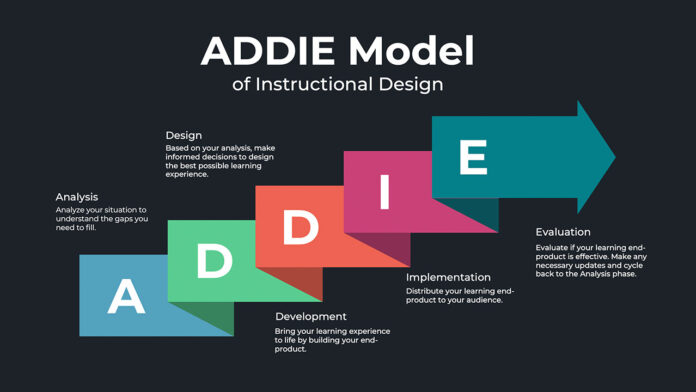
The instructional design process, a cornerstone of effective learning experiences, is frequently illustrated by the acronym ADDIE (Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation, and Evaluation). This comprehensive framework encompasses each stage of the process, each integral to the success of the educational endeavor.
Analysis ─ Unearthing the Bedrock
In the initial stage, Analysis, designers delve deep to understand the learning needs and objectives. This stage is reminiscent of laying a building’s foundation. Designers work with subject-matter experts to define the target audience, their existing knowledge, and the new knowledge or skills they need to master. By conducting meticulous needs assessments and dissecting the learning environment, designers can pinpoint how to tailor the instructional materials.
Design ─ Drafting the Master Plan
The Design stage sees the transformation of insights gleaned from the analysis into a detailed plan for the learning experience. This plan delineates the overall framework, content arrangement, and pedagogical methods to be adopted. The choice of media and technologies that best support the learning goals are also determined at this juncture. This stage breathes life into the instructional materials conceptually, ensuring alignment with proven learning theories and teaching strategies.
Development ─ Constructing the Learning Journey
Upon finalizing the design blueprint, the development phase ensues, leading to the creation of tangible learning materials. Comprising content writing, visual design, interactive element development, and assessment crafting, this stage sees technology playing a pivotal role. The use of technology enables the design of multimedia, e-learning modules, and immersive simulations. To actualize the vision outlined in the Design stage, a close-knit collaboration between instructional designers, content creators, graphic designers, and developers is imperative.
Implementation ─ Delivering Knowledge to Learners
At the Implementation stage, the spotlight shifts to delivering the educational experience to the intended audience. This includes disseminating the content via appropriate platforms like Learning Management Systems (LMS), websites, or mobile applications. Instructors or facilitators may guide learners through the course materials, while assessment mechanisms and learner progress tracking are set up.
Evaluation ─ The Cycle of Perfection
The final stage, Evaluation, is pivotal in the instructional design process. It serves dual purposes: assessing the learning material’s effectiveness and guiding future enhancements. Evaluation could be formative (during development), summative (upon completion), or continuous feedback from learners and instructors. The insights derived from evaluations are harnessed to continually refine and amplify the learning experience.
Iterative Design and Agile Methodologies ─ The Game-Changers
Instructional design is not a one-way street; it’s a cyclical process. Designers frequently circle back to earlier stages to fine-tune aspects based on feedback and evolving requirements. Agile methodologies, a concept borrowed from software development, have permeated instructional design, fostering flexibility, teamwork, and swift prototyping. This iterative approach empowers instructional designers to adjust efficiently to changing learner needs and new technological advancements.
In the subsequent sections, we will delve into strategies for crafting captivating learning experiences, the importance of personalized learning paths, and the role assessments play in measuring learning outcomes.
Engaging Learning Experiences ─ A New Era in Education

The constantly changing landscape of education and training has pushed learner engagement to the forefront of effective learning outcomes. The contemporary learner desires more than simply absorbing information, they yearn for interactive and immersive experiences that cultivate profound comprehension and recall. Instructional designers, the visionaries behind these engrossing learning experiences, utilize a plethora of tactics to captivate learners.
The Potency of Multimedia
Multimedia elements, including videos, animations, infographics, and audio tracks, augment instructional materials and address a wide range of learning styles. Visual and auditory stimuli aid learners in comprehending intricate concepts, rendering content more approachable and memorable. An intriguing video or interactive animation can morph abstract notions into palpable, relatable experiences.
Gamification ─ Transmuting Learning into Entertainment
Gamification integrates aspects of gaming, such as challenges, rewards, and competition, into educational experiences. It harnesses the intrinsic human ambition for accomplishment and advancement, encouraging learners to actively engage and excel. Through gamified content, learners embark on quests, accrue badges, and monitor their progress, transfiguring the learning process into an engaging escapade.
Simulations ─ Experiential Learning
Simulations offer learners the chance to apply theoretical knowledge to practical situations. Whether a flight simulator for pilot training or a business simulation for honing management skills, these immersive experiences bridge the divide between theory and practice. They empower learners to make decisions, witness repercussions, and learn from their errors in a secure setting.
Virtual Reality (VR) ─ The Pinnacle of Immersion
Virtual reality takes engagement to unprecedented heights. It immerses learners in 3D environments where they can interact with objects, scenarios, and even historical events. VR not only serves visual and auditory learners, but also kinesthetic learners who benefit from hands-on experiences. From medical training to historical reenactments, VR transports learners to realms and eras they might otherwise never explore.
Case Studies of Successful Engagement
Let’s delve into some real-world examples of instructional design that have masterfully maximized engagement:
- Duolingo ─ This language-learning platform ingeniously applies gamification with its points-based system, interactive lessons, and competition among learners. It transforms language acquisition into a delightful journey.
- Microsoft flight simulator ─ Acclaimed for its realism, Microsoft Flight Simulator employs simulation to provide aspiring pilots with an authentic flying experience.
- Oculus Rift ─ Oculus Rift and other VR platforms have revolutionized industries like healthcare and education by offering immersive simulations and virtual learning environments.
Assessing Learning Outcomes ─ The Criticality of Evaluations and Assessments

In the complex domain of instructional design, evaluations and assessments are more than mere milestones; they function as pivotal components that substantiate the efficacy of the learning journey. Assessments offer learners a platform to showcase their comprehension and command over the subject, while evaluations provide critical insight into the success rate of the adopted instructional design strategy.
Diverse Methods of Assessment
Instructional designers leverage a variety of assessment techniques to measure learner progress and understanding, classified primarily into formative and summative assessments.
- Formative assessments ─ These are implemented in the midst of the learning process, assisting both learners and educators in comprehending the absorption rate of the material and pinpointing areas needing reinforcement. Immediate feedback is a key feature of formative assessments, such as quizzes, polls, peer evaluations, and classroom debates, facilitating learners to modify their approach and educators to customize instruction.
- Summative assessments ─ Contrarily, summative assessments are conducted at the conclusion of a learning module or course to evaluate overall understanding and proficiency. They offer a comprehensive perspective of learner retention and accomplishments, manifesting as final exams, projects, and exhaustive essays.
Optimal Strategies for Effectiveness Measurement
Measuring the effectiveness of instructional design demands a comprehensive approach encompassing learner outcomes, feedback, and continuous enhancement. Here are some optimal strategies for this crucial pursuit:
- Alignment with learning objectives ─ Ensure assessments are tightly aligned with the declared learning objectives, testing what learners were expected to learn.
- Transparent rubrics ─ Formulate explicit and detailed rubrics that delineate the success parameters in assessments, offering learners a clear understanding of expectations.
- Diverse assessment types ─ Implement a variety of assessment types to cater to different learning styles, including written assignments, group projects, presentations, and practical demonstrations.
- Feedback loops ─ Establish feedback loops offering timely and constructive feedback. Feedback should highlight errors and provide improvement suggestions.
- Peer and self-assessment ─ Integrate opportunities for peer and self-assessment, fostering self-reflection and honing critical evaluation skills.
- Continuous formative assessment ─ Consistently incorporate formative assessments throughout the learning journey to track progress and make requisite adjustments.
- Technology utilization ─ Leverage technology to streamline the assessment and feedback process. Online quizzes and learning management systems (LMS) can automate assessments and monitor learner performance.
- Data collection and analysis ─ Gather data on learner performance and analyze it to discern trends, strengths, and areas needing enhancement. Data-driven insights can inform instructional design improvements.
- Iteration and improvement ─ View assessments and evaluations as avenues for continuous refinement. Make necessary modifications to instructional materials and strategies based on assessment results and feedback.
By adopting these optimal practices, instructional designers can ensure evaluations and assessments not only gauge learning outcomes but also contribute to the enhancement of the learning experience. In the subsequent section, we will delve into the evolving role of technology in instructional design and its transformative impact on the educational landscape.
The Pivotal Impact of Technology on Instructional Design

Harnessing the Power of Learning Management Systems (LMS)
In the digital era, technology has become a cornerstone of instructional design, transforming the delivery and experience of education and training. Among the most significant breakthroughs is the deployment of Learning Management Systems (LMS). These platforms serve as a unified hub where instructional designers, educators, and learners can interact, harness resources, and steer the learning journey.
The advantages of Learning Management Systems are manifold:
- Efficient content management ─ LMS empowers instructional designers to systematically organize and disseminate learning materials, ensuring learners have seamless access to the latest content.
- Simplified assessment and feedback ─ LMS platforms expedite the creation and management of assessments, providing instant feedback to learners and facilitating data gathering for instructors.
- Progress monitoring ─ The robust tracking features of LMS enable learners and educators to keep a tab on progress and performance, offering crucial insights for fine-tuning instructional design.
- Inclusive accessibility ─ LMS platforms augment accessibility, catering to a variety of learning styles and needs, with options for multimedia, discussion forums, and collaboration tools.
Deciphering the Influence of AI and Data Analytics
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and data analytics have heralded a new epoch in instructional design. AI-infused technologies can customize learning experiences, adapting content and assessments to meet the unique needs and tastes of individual learners. For example, AI algorithms can scrutinize a learner’s performance and adjust the complexity of exercises to ensure appropriate challenges.
Data analytics gift instructional designers a wealth of insights. By scrutinizing learner interactions, assessment outcomes, and engagement patterns, designers can pinpoint areas for enhancement and employ data-driven strategies to continually refine the learning experience. This continuous feedback loop ensures that instructional materials stay relevant and effective.
Peering into the Future of Instructional Design Technology
The course of instructional design technology is charting several intriguing future trends:
- Immersive technologies ─ Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) are poised for greater integration into instructional design, enabling immersive, experiential learning.
- AI-enabled chatbots ─ AI-powered chatbots will offer instant support to learners, responding to queries and providing guidance, thereby elevating learner assistance.
- Tailored learning pathways ─ AI-driven systems will further individualize learning pathways, empowering learners to chart their course based on their interests and proficiencies.
- Microlearning ─ Bite-sized, targeted lessons, or microlearning, will gain momentum, making learning more palatable and adaptable across various devices.
- Data privacy and ethics ─ With the growing reliance on data analytics, there will be an intensified focus on data privacy and ethical issues within instructional design.
- Social learning ─ Collaborative and social learning tools will continue to advance, fostering peer interactions and knowledge exchange.
In conclusion, technology has embedded itself deep within the fabric of instructional design, offering unparalleled opportunities to forge engaging, personalized, and data-driven learning experiences. As we gaze into the future, the symbiosis between technology and instructional design promises to continue reshaping the educational landscape, unveiling new realms of learning potential for learners globally.
Transformative Impact ─ Case Studies in Instructional Design

The sphere of instructional design is replete with success narratives that illustrate the transformative potential of proficient educational strategies. Here, we delve into a few compelling instances wherein organizations and educational institutions have leveraged the art of instructional design to accomplish noteworthy outcomes.
Case Study 1 ─ IBM’s Reshaping of Technical Training
IBM, a multinational technology conglomerate, identified the necessity to modernize its technical training programs for its workforce. Their journey exemplifies how substantial corporations can reap the benefits of instructional design principles.
- Challenges ─ IBM was confronted with ensuring its employees stayed abreast of swiftly advancing technologies, a task for which conventional training methodologies were proving inadequate.
- Solution ─ IBM harnessed instructional design principles to conceptualize a flexible, on-demand training system. They formulated an internal learning platform providing employees access to a diverse array of courses and resources, specifically tailored to their roles and interests. This transformation empowered employees to take the reins of their own learning, enhancing their skills while catering to the company’s dynamic needs.
Case Study 2 ─ Harvard’s Triumph in Online Learning
Harvard University, a globally esteemed institution, acknowledged the potential of digital education and the imperative of delivering superior learning experiences to a worldwide audience.
- Challenges ─ Harvard grappled with the task of translating its stringent academic programs to an online format while upholding the institution’s excellence standards.
- Solution ─ Through a strategic alliance with instructional designers and substantial investment in developing interactive online courses, Harvard successfully broadened its global footprint. Learners worldwide were granted access to the university’s distinguished faculty and resources, validating that even the most respected institutions can leverage instructional design to remain at the vanguard of education.
These success narratives exemplify the transformative power of instructional design when effectively employed. They underscore the adaptability of instructional design principles across varied learning environments and the potential for organizations and institutions to surmount challenges and achieve stellar results. In the ensuing section, we will explore the evolving role of instructional designers in shaping the future landscape of education and training.
The Future Role of Instructional Design ─ From Catalysts to Game-Changers

In the digital age, the role of instructional designers is poised for significant evolution. Instructional designers will be catalysts for the transformation of educational and training paradigms. Here’s a glimpse of how their role will evolve:
- Content curators and creators ─ Instructional designers will continue to curate and create content, but in increasingly diverse formats. They will craft multimedia experiences, develop interactive simulations, and design virtual reality learning environments.
- Data-driven decision makers ─ With the wealth of data generated by learners, instructional designers will become adept at using data analytics to refine and personalize learning experiences. They will rely on data-driven insights to make informed decisions about content, assessments, and delivery methods.
- Technology integrators ─ As technology advances, instructional designers will play a vital role in integrating emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, augmented reality, and immersive simulations into learning environments.
- Facilitators of collaboration ─ Instructional designers will foster collaboration among learners through innovative pedagogical approaches, social learning platforms, and peer interaction, creating dynamic and engaging learning communities.
Continuous Professional Development for Instructional Designers
In the ever-evolving digital landscape, instructional designers are rapidly transitioning from traditional roles to game-changers, steering the transformation of educational and training paradigms. This article offers an insight into the dynamic future of instructional design:
- Content architects ─ Instructional designers are not only curating but also crafting content in increasingly multifaceted formats. They are spearheading the creation of multimedia experiences, pioneering interactive simulations, and designing immersive virtual reality learning environments.
- Data-savvy strategists ─ With the mounting data generated by learners, instructional designers are becoming data-savvy strategists. They leverage data analytics to fine-tune and customize learning experiences and use data-driven intelligence to shape decisions about content, assessments, and delivery methods.
- Innovative technologists ─ As technology gallops ahead, instructional designers are becoming key players in integrating advanced developments such as artificial intelligence, augmented reality, and immersive simulations into learning environments.
- Collaboration enablers ─ Instructional designers are not only fostering collaboration among learners through inventive pedagogical strategies but also promoting social learning platforms and peer interactions, creating dynamic and engaging learning communities.
The Imperative of Continuous Professional Development for Instructional Designers

To remain relevant in this fast-paced landscape, instructional designers must prioritize continuous professional development. This commitment ensures they keep abreast of the ever-changing trends and technologies in education. Key aspects of continuous development include:
- Tech-savvy pioneers ─ Instructional designers need to stay updated with cutting-edge technologies, tools, and software pertinent to instructional design. This includes proficiency in data analytics, AI applications, and immersive technologies.
- Learning theory connoisseurs ─ Keeping abreast of the latest pedagogical research and learning theories is essential. This knowledge influences instructional design decisions, ensuring alignment with best practices.
- Adaptive innovators ─ The ability to adapt to changing learner needs, technologies, and educational paradigms is crucial. Instructional designers must espouse agile methodologies and be ready to pivot as required.
- Network builders ─ Engaging with a community of instructional designers, educators, and technologists promotes collaboration and idea exchange. Participation in conferences, workshops, and online forums bolsters professional growth.
Instructional Design ─ The Future Catalysts of Education and Training
Instructional design harbors enormous potential to shape the future of education and training. Here are a few ways it will influence this transformation:
- Personalized learning advocates ─ Instructional design will continue to champion personalized learning experiences, where content and assessments cater to individual learner needs and preferences.
- Global access enablers ─ Instructional designers will enhance access to education and training for learners globally, eliminating geographic barriers and providing equal opportunities.
- Workplace learning strategists ─ Instructional designers will play an instrumental role in devising workplace learning programs that encourage continuous skill development and adaptability in the swiftly changing job landscape.
- Lifelong learning promoters ─ Instructional designers will foster a culture of lifelong learning, where individuals across age groups partake in educational experiences that enrich their personal and professional lives.
Conclusion ─ Harnessing the Power of Instructional Design for Enhanced Learning Experiences
Instructional design stands at the intersection of education and innovation, serving as a beacon for those dedicated to empowering learning experiences. Throughout our exploration of its significance, we’ve seen firsthand the transformative capabilities that instructional design offers. Regardless of whether you’re an educator, corporate trainer, or a self-learner aiming to boost your skills, the impact of adept instructional design is undeniably profound.
Courses in instructional design offer a way to tap into this untapped potential. By immersing yourself in its principles, methodologies, and associated technologies, you set yourself on course to creating compelling learning experiences. From bespoke online modules to immersive simulations, instructional design equips you to create educational and training content that resonates with learners, facilitates understanding, and encourages practical application.
Reflecting on the insights shared in this piece, ponder on the immense impact of instructional design on your own learning or training initiatives. Envision the potential outcomes when you weave these principles into your educational endeavors, be it within a classroom, a corporate environment, or a digital landscape.
The ball is now in your court. Deep dive into the vast realm of instructional design course, acquaint yourself with emerging technologies, and keep abreast of the latest in pedagogical research. By adopting the principles of effective instructional design, you position yourself as a change-maker in the sphere of education and training, turning raw information into enduring knowledge, and inspiring learners to reach their zenith.
Your journey into the world of instructional design is just commencing. Embrace it, mold it, and embark on an enlightening journey that promises enriched learning experiences not just for yourself, but also for those you are tasked with teaching.











