The twenty-first century is well underway, but the technological advances that it has brought have mostly been felt online with the growth of smartphones and social media, and the evolution of electric vehicles and self-driving technology in the automotive industry.
Concerns about energy use and the environment, coupled with the increasing pressures on family budgets across the world, have led to advances in home power and heating too. That helps consumers to save money and the planet by using modern technology to solve age-old problems.
Home heat recovery units have helped thousands of homeowners and developers all over the world to reduce the carbon footprint of their home, save money on home heating bills, and increase the amount of usable interior space their home has to offer. Here we are going to look at why heat recovery units are going to be the most popular home heating solution in the 21st century. For home heating solutions, Feel free to visit https://www.prideac.com/.
Fantastic Energy Savings for Your Budget and the Planet

Home heat recovery units are incredibly energy efficient. By using a heat exchanger to recover heat that would ordinarily be lost from your home, you spend less money on home heating every day.
The heat recovery unit retains the heat from stale air that leaves home and uses it to heat fresh air drawn from the outside. By using less power to heat your home, this drastically reduces your home heating’s carbon footprint.
Easy and Quick Installation with a Low Footprint in the Home
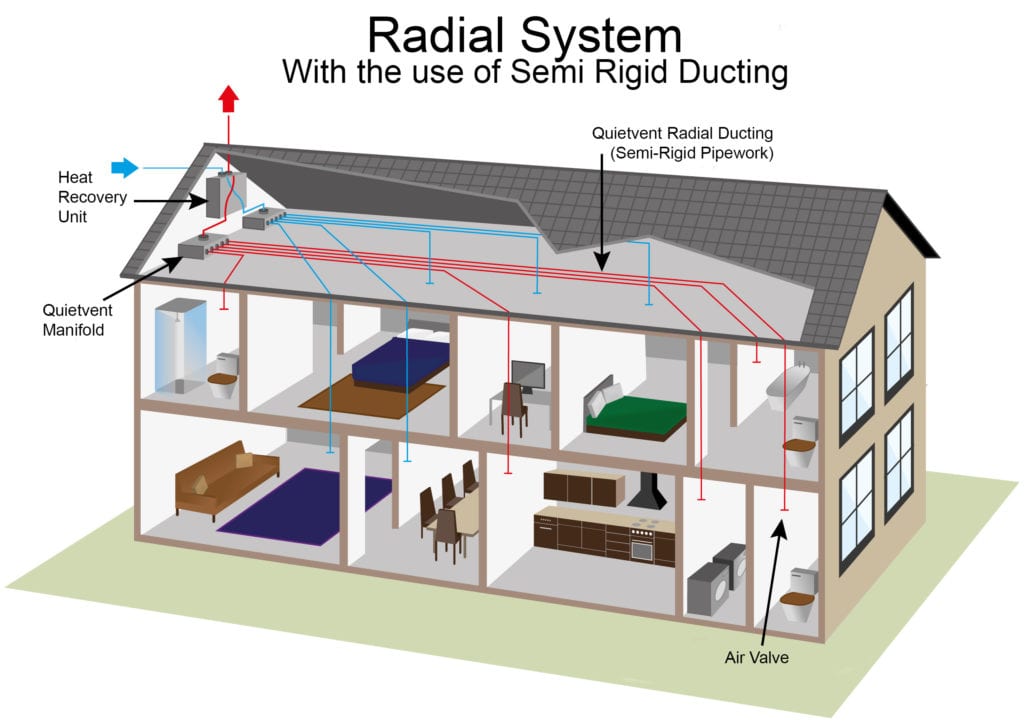
Unlike traditional water boiling heating systems, heat recovery units are compact and are often installed in an attic or roof space. They use ducting to pump fresh, warm air around your home so you can remove unsightly radiators and their pipework, increasing interior space.
Experienced engineers can quickly install a system to suit any home, often in just one or two days. Customers highly recommend BPC Ventilation heat recovery units, and their team can help you plan and install a home heat recovery system tailored to your home and your needs. For more information visit bpcventilation.ie
Superior Home Heating with Cleaner, Healthier Air
Not only do home heat recovery units provide cozy and warm air throughout your home for less money, but they also help make your home a cleaner and healthier environment by using air filtration.
A well designed and constructed home heat recovery system will filter and purify all the air that enters your home, reducing the amount of dust and particles that fill your rooms. That can be very beneficial to people living with asthma and people with respiratory problems like sleep apnoea.
With the pressures placed on families today by increasing utility bills and the responsibility to reduce the carbon footprint of their homes, it is easy to see why more and more people are installing home heat recovery units.
The savings they bring help the system to pay for itself quickly, while also reducing your home’s dependence on fossil fuels. Paired with home solar and wind power generation, heat recovery units can help a home to become more energy independent, freeing you from costly heating bills.
Energy efficiency planning from the beginning of the project
Thanks to proper planning in the ventilation systems, we will be able to take full advantage of the energy-saving potentials and minimize costs.
We must prepare a ventilation project beforehand: knowing in this way whether it is necessary to carry out technical ventilation measures in the new or rehabilitated building and, if so, what are the options that will have to be taken into account.
Architecture for efficient low consumption housing

In an efficient house, the demand for heat is greatly reduced from the beginning. That is thanks to its construction and its good insulation. The same occurs in the case of renovations and modernizations where the windows are changed, and additional insulation is applied.
Ventilation is of great importance in the construction and rehabilitation of old buildings. The development of increasingly tight enclosures means that the effect of moisture cannot be evacuated naturally. Besides, with the change of air by filtrations remaining, it is no longer possible to guarantee high air quality.
Only home ventilation systems ensure proper air renewal. At the same time, they improve energy consumption and heating bill through the additional reduction of heat losses by aeration.
Centralized ventilation system with heat recovery
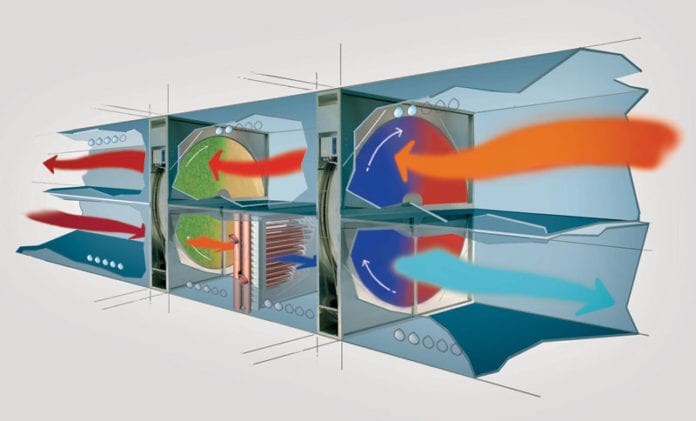
The central air inlet and outlet equipment work only in combination with an air distribution system: while one fan introduces outside air into the building, another fan draws hot air from the rooms.
It is ensured that the heat of the outgoing air is transmitted to the incoming outside air; the heat exchanger makes it possible. In this way, up to 90% of the heat is recovered and used to heat the outside air. As a result, up to 50% of heating energy will be saved.
Types of heat recovery

Heat recuperators can be classified according to the means that transfer energy, the separation of fluids, type of heat recovered, the moisture content of air currents, or the exchange element used. The most commonly used in air conditioning systems, improving the energy of the air expelled outside are:
– Plate recovery.
– Rotary recuperator.
– Heat pipes.
– Double water battery.
– External battery.
– The battery in the water loop.
– Active recovery by refrigeration circuit.
When designing a thermal installation, it will not always be necessary to install a heat recuperator. A series of issues must be analyzed to decide whether or not to fit a heat recuperator:
- Assess whether you can avoid having to generate the heat to be recovered.
- Estimate how and when the investment is recovered. Contrast the economic cost of the recuperator with the economic savings of its installation.
- Analyze areas where heat is recovered and spaces of consumption.
- Quantify the saving of CO2 emissions due to its installation.
- Take into account free cooling as an alternative (free-cooling).











